TECHNICAL INFORMATION
Metals that can be deposited
In this section, we are going to introduce the type of metals that can be deposited by electroplating/electroless plating.
*Plating in this article refers to wet plating.
1. Electroplating
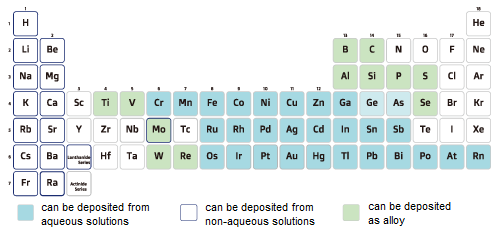
Alkali metals and alkaline-earth metals are electrodeposited only as oxides or hydroxides due to their ionization tendency, and Al, Ti, and rare earth metals are electrodeposited only as oxides or hydroxides due to their strong bonding with oxygen, making electrodeposition from aqueous solution impossible. Such metals are electrodeposited using organic solvents or molten salts (special orders are available). For Al in particular, electrodeposition using ionic liquids is also available. Among metals that can be electrodeposited in aqueous solution, soluble anodes are generally used for Zn, Ag, Cu, Cd, Fe, Ni, and Co.
*Metals such as As and Ge are described differently in some literature.
2. Electroless Plating
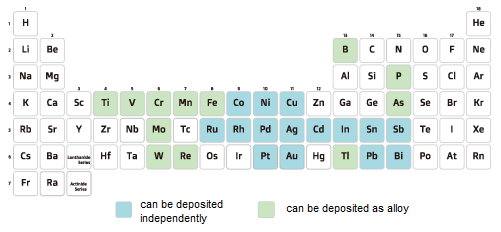
There are several typical types of electroless plating film, such as copper and nickel, etc. Deposition is possible by selecting a reducing agent corresponding to each metal species. Electroless plating proceeds at a mixed potential due to the simultaneous reaction of the reduction reaction of the metal complex (cathode) and the oxidation reaction of the reducing agent (anode), so it is necessary to select a reducing agent with a redox potential (reversible potential) lower than the reversible potential of the metal complex.
Currently, the following five types of reducing agents are mainly used for plating.
→hypophosphite, formaldehyde, borohydride, DMAB, and hydrazine
References
The Chemical Society of Japan (ed.), “Electrochemistry of Interfaces from the Viewpoint of the Molecular Level” (Gakkai Shuppan Center, 1975)
Toru Watanabe, “Nanoplating” (Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, 2004)
Shiro Haruyama, “Electrochemistry for Surface Engineers, 2nd Edition” (Maruzen, 2005)






